Revolutionizing Sciatica Pain Relief: An Expert Overview of Orthopedic Procedures in 2024
In 2024, the landscape of orthopedic interventions for sciatica has evolved significantly, integrating advanced minimally invasive techniques with precision diagnostics that underscore personalized treatment pathways. Sciatica, characterized by neuropathic pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, demands a nuanced approach that balances symptom relief with long-term functional restoration. Orthopedic surgeons now leverage cutting-edge modalities that address the root biomechanical and neurological etiologies, transcending traditional decompression surgeries.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Precision and Reduced Morbidity
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) has emerged as a cornerstone for treating sciatic pain caused by lumbar disc herniation or spinal stenosis. This approach employs endoscopic visualization and tubular retractors, which limit soft tissue disruption and reduce postoperative inflammation. The advantages include decreased hospital stays, faster recovery, and diminished risk of adjacent segment disease. Recent data from the Journal of Spine Surgery corroborate the efficacy of MISS in delivering sustained pain relief and functional improvement compared to open laminectomy.
How Do Emerging Orthopedic Procedures Compare in Managing Complex Sciatica Cases?
Complex sciatica cases, particularly those involving nerve root entrapment with concomitant degenerative changes, challenge conventional treatment algorithms. Advanced procedures such as percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) and spinal cord stimulation (SCS) have garnered attention for their targeted relief mechanisms. PELD utilizes high-definition optics and laser ablation to excise herniated disc material with minimal collateral damage, whereas SCS modulates neuropathic pain pathways through electrical impulses, offering a reversible and adjustable solution. Choosing between these modalities depends on patient-specific factors, including anatomical considerations and previous treatment responses.
Integrating Multidisciplinary Approaches with Surgical Innovations
Orthopedic care for sciatica in 2024 increasingly emphasizes a multidisciplinary model combining surgical precision with rehabilitative strategies. Postoperative orthopedic rehabilitation, tailored to optimize lumbar stabilization and neurodynamic mobilization, significantly enhances outcomes. Clinics specializing in coordinated care, such as the NJ Multidisciplinary Orthopedic Clinics, exemplify this integrative approach, reducing recurrence rates and accelerating functional recovery.
Exploring Non-Surgical Alternatives Complementing Orthopedic Interventions
While surgery remains pivotal for refractory sciatica, non-surgical treatments like epidural steroid injections and orthopedic-trigger point injections serve as adjuncts or alternatives in select cases. Understanding their role in the comprehensive care continuum is imperative for clinicians aiming to optimize patient-specific protocols. For detailed guidance on injection techniques, see the step-by-step orthopedic trigger point injection procedure resource.
Curious About Advanced Orthopedic Techniques for Sciatica? Join the Expert Dialogue
Healthcare professionals and patients alike are encouraged to deepen their understanding by exploring specialized content such as minimally invasive back pain treatments and sharing clinical experiences to refine the collective knowledge base. Engaging in these discussions fosters continuous improvement in sciatica management protocols.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools Enhancing Sciatica Treatment Precision
In 2024, the integration of advanced imaging techniques such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and functional MRI (fMRI) has significantly refined the diagnostic accuracy for sciatica. These modalities enable orthopedic specialists to visualize nerve root integrity and inflammation in unprecedented detail, facilitating personalized surgical planning and non-invasive treatment selection. The capability to map nerve fiber disruptions supports targeted interventions, mitigating the risks of overtreatment or insufficient decompression.
What Role Does Artificial Intelligence Play in Optimizing Orthopedic Sciatica Management?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are increasingly incorporated into orthopedic practice, assisting in predictive analytics for treatment outcomes and risk stratification. AI-powered platforms analyze vast datasets from patient histories, imaging, and genetic markers to suggest optimal intervention strategies. This technology not only accelerates decision-making but also enhances patient-specific care plans by anticipating complications or recurrence. For clinicians exploring AI applications, resources like the Arthritis Foundation’s insights on AI in orthopedics provide valuable guidance.
Customized Rehabilitation Protocols Post-Operative Sciatica Treatment
Postoperative care now emphasizes bespoke rehabilitation programs tailored to the individual’s surgical procedure, baseline function, and lifestyle demands. Integrating neurodynamic exercises, proprioceptive training, and pain neuroscience education, these protocols accelerate neural recovery and functional reintegration. Collaboration between orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, and pain specialists ensures continuity of care, addressing both mechanical and neuropathic components of sciatica.
For patients undergoing lumbar fusion or other spinal surgeries, exploring rehabilitation tips at Orthopedic Rehab Tips After Lumbar Fusion Surgery can optimize recovery trajectories.
Emerging Non-Invasive Technologies: Beyond Traditional Orthopedic Interventions
Innovations such as non-invasive spinal decompression therapy and wearable neuromodulation devices are reshaping non-surgical sciatica management. These technologies offer continuous, adjustable pain modulation and mechanical decompression without inpatient stays or surgical risks. Their incorporation into early-stage treatment algorithms aims to reduce progression to invasive procedures and improve quality of life.
Engage with the Community: Share Your Insights and Experiences
We invite clinicians, researchers, and patients to contribute to the evolving discourse on advanced orthopedic sciatica care. Sharing clinical outcomes, rehabilitation successes, or challenges encountered with emerging treatments enriches the collective expertise. Join the conversation by commenting below or sharing this article with peers committed to advancing orthopedic spine health.
Biomechanical Innovations: Tailoring Orthopedic Interventions for Sciatica’s Complex Dynamics
Recent advances in biomechanical modeling and patient-specific simulation have revolutionized how orthopedic surgeons approach sciatica treatment. Utilizing finite element analysis (FEA), surgeons can predict spinal load distribution and neural tension under various postural conditions, guiding more precise surgical targeting and implant selection. This approach mitigates the risk of iatrogenic instability while optimizing decompression efficacy. Furthermore, custom 3D-printed interbody cages and facet joint spacers have emerged, designed from patient imaging data to restore native spinal alignment and preserve segmental motion, thereby reducing adjacent segment degeneration.
How Does Biomechanical Modeling Enhance Surgical Outcomes in Sciatica Patients?
Biomechanical modeling offers a transformative lens through which surgeons visualize and quantify spinal mechanics preoperatively. By simulating surgical scenarios, it allows for optimization of implant size, shape, and placement to minimize mechanical stress on adjacent tissues. This leads to tailored interventions that consider individual anatomical variability and pathology severity, improving long-term functional outcomes and minimizing revision rates.
According to a 2023 study published in The Spine Journal, patients whose surgical plans incorporated biomechanical simulations demonstrated significantly better postoperative pain scores and mobility metrics compared to conventional planning methods.
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Predictive Analytics: Shaping Personalized Sciatica Management Plans
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into orthopedic practice extends beyond diagnostics to encompass predictive analytics that refine personalized treatment algorithms. Machine learning models analyze multifactorial datasets including imaging features, genetic markers, and patient-reported outcomes to forecast surgical risks, recovery trajectories, and potential complications with remarkable accuracy. These insights empower clinicians to tailor perioperative strategies, optimize rehabilitation protocols, and engage patients with transparent prognostic information.
For example, AI-driven decision support systems aid in determining candidacy for minimally invasive procedures versus conservative management, balancing efficacy with patient safety. This precision medicine approach aligns with contemporary trends towards value-based care and outcome optimization.
What Are the Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy Challenges in Applying AI to Orthopedic Sciatica Care?
While AI promises transformative benefits, it also raises critical ethical and data privacy concerns. Ensuring algorithmic transparency, mitigating biases embedded in training data, and safeguarding patient confidentiality are paramount. Orthopedic practitioners must advocate for robust regulatory frameworks and engage in interdisciplinary collaborations with data scientists to uphold ethical standards. Moreover, informed consent processes should explicitly address AI utilization in clinical decision-making to maintain patient autonomy and trust.
Neuroplasticity and Pain Modulation: Advanced Insights Guiding Rehabilitation Protocols
Emerging research underscores the role of central nervous system neuroplasticity in chronic sciatica pain persistence. Rehabilitation paradigms now incorporate cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and graded motor imagery (GMI) alongside physical modalities to retrain maladaptive neural circuits. Pain neuroscience education empowers patients to reconceptualize their pain experience, reducing fear-avoidance behaviors and facilitating engagement in active recovery.
Combining neurodynamic mobilization with these psychosocial interventions fosters a holistic recovery process that addresses both peripheral and central contributors to sciatica. This multidisciplinary approach is supported by recent clinical trials demonstrating superior functional outcomes and reduced opioid dependency.
Future Directions: Integrating Wearable Biosensors and Real-Time Feedback in Sciatica Management
Wearable biosensors capable of monitoring biomechanical parameters and neuromuscular activity in real-time are poised to revolutionize postoperative and non-surgical sciatica care. These devices provide continuous feedback on movement patterns, muscle activation, and posture, enabling personalized adjustments to rehabilitation exercises and activity levels. Early detection of aberrant biomechanics or pain flare-ups can prompt timely clinical interventions, potentially averting chronicity and recurrence.
Integration with mobile health platforms facilitates patient engagement and adherence, fostering a data-driven, patient-centered care continuum. Ongoing research aims to validate efficacy and scalability of these technologies within diverse patient populations.
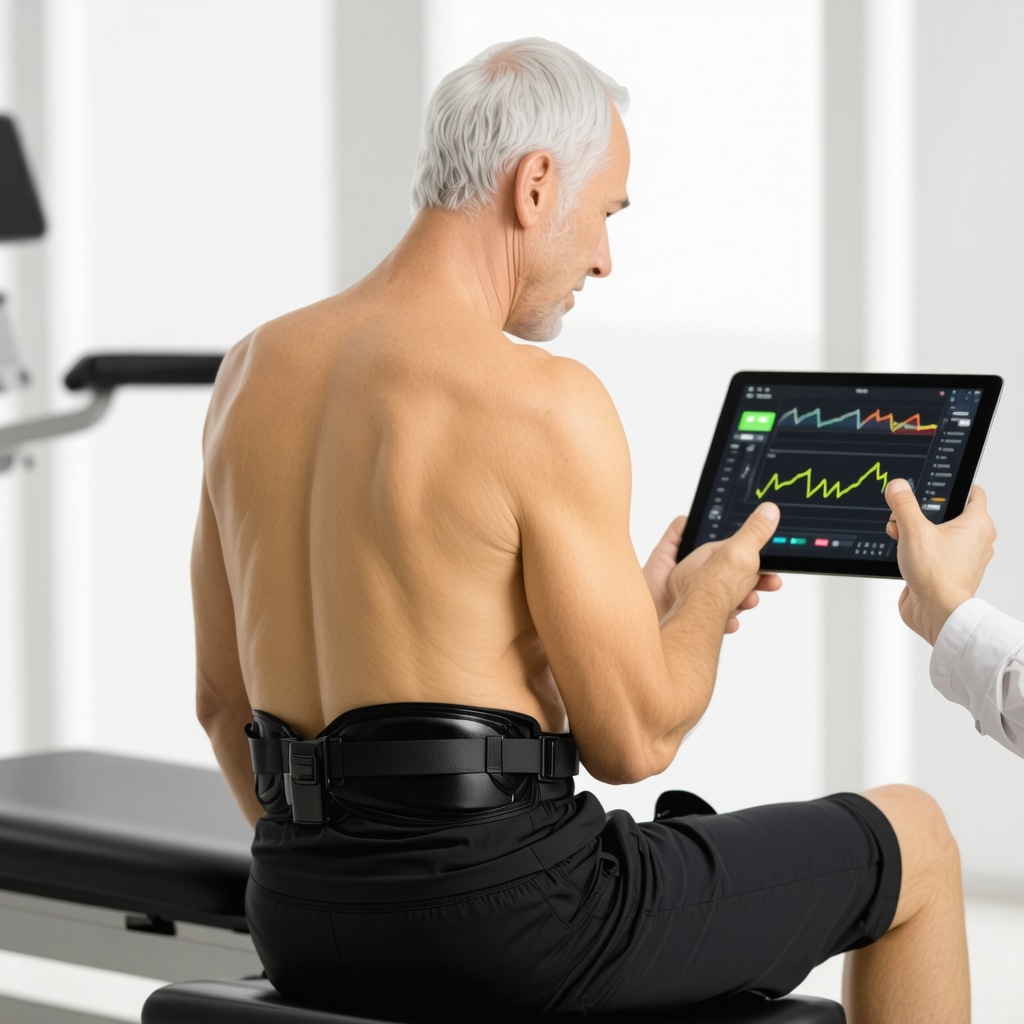

How Can Wearable Technologies Be Seamlessly Integrated into Orthopedic Sciatica Rehabilitation?
Successful integration of wearable technologies requires multidisciplinary collaboration between orthopedic specialists, physical therapists, and technology developers. User-friendly interfaces and tailored feedback algorithms are essential to ensure patient compliance and meaningful clinical insights. Moreover, addressing data security and interoperability with electronic health records remains a priority to harness the full potential of these innovations.
Clinicians interested in pioneering these advancements are encouraged to explore partnerships with technology innovators and participate in pilot programs to refine wearable applications in real-world settings.
Harnessing AI-Driven Decision Support for Complex Sciatica Cases
In the constantly evolving realm of orthopedic sciatic care, artificial intelligence (AI) has transcended basic diagnostic support to become an integral tool in crafting bespoke treatment regimens. State-of-the-art AI algorithms now assimilate multifaceted patient datasets—ranging from high-resolution imaging and genomic profiles to longitudinal symptom tracking—to predict therapeutic responsiveness and stratify surgical risk with unprecedented precision. This paradigm shift enables clinicians to tailor interventions that harmonize efficacy with patient safety, particularly in multifactorial and refractory sciatica presentations.
Biomechanical Simulation: The New Frontier in Surgical Personalization
Finite element modeling and patient-specific biomechanical simulations have revolutionized preoperative planning by allowing surgeons to visualize spinal load dynamics and neural tissue strain under various physiological conditions. This sophisticated approach informs implant selection, surgical approach, and decompression extent to mitigate iatrogenic complications and optimize biomechanical restoration. The integration of 3D-printed custom implants further complements these efforts, ensuring anatomical congruency and functional preservation.
Integrating Wearable Biosensors: Real-Time Insights into Rehabilitation Efficacy
Wearable technologies equipped with biosensors enable continuous monitoring of neuromuscular activation patterns, spinal kinematics, and patient adherence to prescribed rehabilitation protocols. These devices facilitate dynamic feedback loops between patients and care teams, allowing timely modifications to therapy and early detection of maladaptive movement patterns that could precipitate symptom recurrence.
How Can AI and Biomechanical Innovations Be Synergistically Applied to Enhance Sciatica Surgical Outcomes?
The synergistic application of AI and biomechanical modeling represents a cutting-edge frontier in sciatica management. AI-driven analytics can interpret biomechanical simulation outputs to refine surgical planning by identifying optimal decompression strategies and implant configurations tailored to individual anatomy and pathology. This convergence fosters predictive modeling of postoperative functional trajectories and complication probabilities, guiding shared decision-making and personalized care pathways.
To delve deeper into these advancements, consult the detailed analyses provided by the Spine Journal’s 2023 biomechanical and AI integration study, which elucidates the tangible impact on patient outcomes.
Addressing Ethical and Data Governance Challenges in AI-Enhanced Orthopedic Care
Despite the transformative potential of AI, orthopedic practitioners must navigate complex ethical landscapes encompassing data privacy, algorithmic bias, and informed consent. Implementing transparent AI frameworks and robust cybersecurity protocols is vital to maintaining patient trust and regulatory compliance. Multidisciplinary collaboration with data ethicists and legal experts ensures that AI deployment aligns with evolving healthcare standards and respects patient autonomy.
Embracing Neuroplasticity-Centric Rehabilitation: A Paradigm Shift
Contemporary rehabilitation strategies increasingly leverage insights into central nervous system neuroplasticity, integrating cognitive behavioral therapy and graded motor imagery with conventional physical therapies. This holistic approach targets maladaptive pain processing pathways, fostering durable recovery and reducing reliance on pharmacologic interventions.
Engage with Advanced Orthopedic Innovations Today
Clinicians and researchers are invited to actively participate in advancing orthopedic sciatica management by integrating AI, biomechanical modeling, and wearable technology into clinical practice. Sharing clinical outcomes and collaborating on pilot programs will accelerate the refinement of these transformative modalities. Engage with the latest research and contribute to this dynamic field by reaching out to specialized multidisciplinary orthopedic centers.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Integrating AI and Biomechanical Modeling Elevates Surgical Precision
The convergence of artificial intelligence with patient-specific biomechanical simulations is transforming sciatica surgical planning. By leveraging AI to interpret complex biomechanical data, surgeons can customize decompression techniques and implant designs to individual anatomy and pathology severity, thereby minimizing complications and enhancing long-term outcomes.
Neuroplasticity-Focused Rehabilitation Enhances Pain Modulation
Incorporating cognitive-behavioral therapy and graded motor imagery alongside physical rehabilitation addresses central sensitization mechanisms in chronic sciatica. This multidisciplinary approach promotes durable pain relief, reduces opioid reliance, and facilitates active patient engagement in recovery.
Wearable Biosensors Enable Real-Time, Data-Driven Rehabilitation Adjustments
Wearable technologies equipped with neuromuscular and biomechanical sensors provide continuous feedback on patient adherence and movement quality. This allows clinicians to promptly modify rehabilitation protocols, detect early signs of maladaptive patterns, and optimize functional recovery trajectories.
Ethical Stewardship is Essential in AI-Enhanced Orthopedic Care
While AI offers remarkable benefits, addressing algorithmic bias, data privacy, and transparency is critical. Orthopedic professionals must champion ethical frameworks and informed consent processes to maintain patient trust and ensure equitable care delivery.
Multidisciplinary Care Models Amplify Outcomes in Complex Sciatica Management
Combining surgical innovations with coordinated rehabilitation and pain management strategies results in superior patient outcomes. Clinics embracing this integrative model, such as those highlighted in the NJ Multidisciplinary Orthopedic Clinics, demonstrate reduced recurrence and expedited functional restoration.
Curated Expert Resources
The Spine Journal: A leading peer-reviewed publication offering in-depth studies on biomechanical modeling and AI integration in spine surgery, essential for understanding cutting-edge surgical innovations.
Arthritis Foundation’s AI in Orthopedics Insights: Provides authoritative guidance on ethical AI applications and emerging technologies within orthopedic care.
Orthopedic Trigger Point Injection Procedure Guide: A comprehensive resource detailing advanced injection techniques that complement surgical interventions, available at step-by-step orthopedic trigger point injection procedure.
Orthopedic Rehab Tips After Lumbar Fusion Surgery: Expert advice on tailored postoperative rehabilitation protocols that optimize recovery, accessible via Orthopedic Rehab Tips After Lumbar Fusion Surgery.
NJ Multidisciplinary Orthopedic Clinics Insights: Showcases integrative care models that demonstrate best practices in combining surgical and rehabilitative strategies for sciatica, featured at NJ Multidisciplinary Orthopedic Clinics.
Final Expert Perspective
Advancements in orthopedic procedures for sciatica pain relief in 2024 underscore a paradigm shift toward precision medicine powered by AI, biomechanical innovation, and neuroplasticity-informed rehabilitation. This integrative framework not only refines surgical accuracy but also enhances patient-centered recovery and long-term functional success. Embracing ethical considerations and multidisciplinary collaboration remains pivotal to maximizing these benefits. Professionals seeking to deepen their expertise are encouraged to engage with leading resources, participate in evolving clinical dialogues, and explore specialized centers like the top orthopedic spine specialists to trust in 2025. For personalized guidance or to contribute insights, visit Contact Us to connect with experts shaping the future of sciatica care.


This article provides an impressive overview of how advanced technology is transforming sciatica treatment in 2024. The integration of AI and biomechanical modeling particularly caught my attention, as these innovations seem to significantly improve surgical planning and patient outcomes. I’ve seen firsthand how personalized approaches, like 3D-printed implants and real-time biosensor feedback, can make a real difference in recovery speed and pain relief. One challenge I’ve encountered is ensuring these cutting-edge interventions are accessible to patients across different healthcare settings. Do you think these technologies will become widely available soon, or will cost and training barriers slow their adoption? It’s an exciting time in orthopedic care, and I’m eager to see how these tools continue to evolve and improve quality of life for sciatica sufferers.