Unlocking the Mystery: What Makes Facet Joint Pain So Challenging?
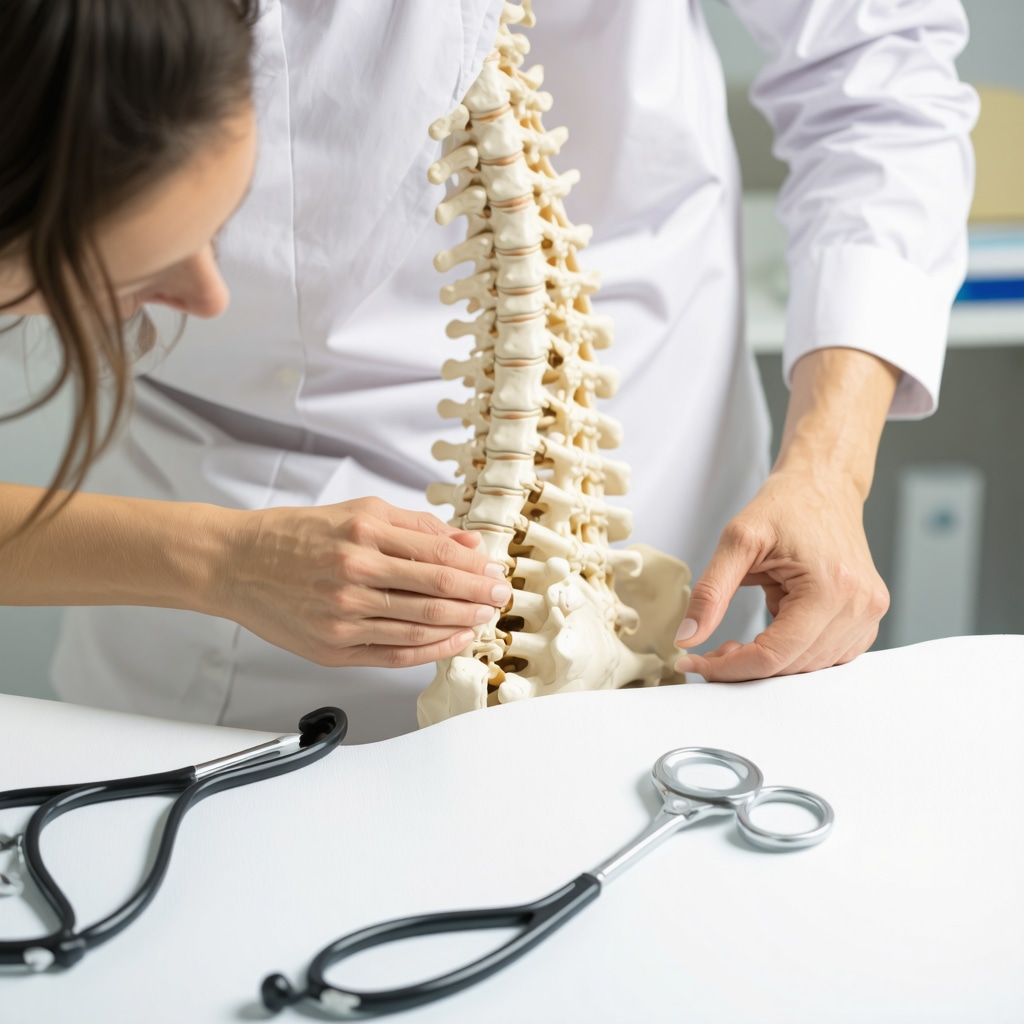
Facet joint pain, often underestimated, is a complex condition resulting from inflammation or degeneration of the small joints connecting vertebrae. Unlike general back pain, facet joint discomfort can be sharp, localized, and aggravated by specific movements, making accurate diagnosis and treatment crucial. Patients frequently report stiffness and deep aching sensations that hinder daily activities, highlighting the importance of targeted orthopedic interventions.
Precision in Orthopedics: Tailoring Treatments Beyond the Surface
Effective management of facet joint pain demands a nuanced approach that considers the joint’s biomechanical function and individual patient factors. Non-surgical options like physical therapy focus on strengthening supporting musculature and improving spinal flexibility, which can significantly reduce joint stress. For instance, a case study published in the National Center for Biotechnology Information highlights how a combined regimen of manual therapy and targeted exercises helped patients achieve substantial pain relief without invasive procedures.
How Do Orthopedic Specialists Determine the Best Treatment Path for Facet Joint Pain?
Orthopedic experts employ a combination of detailed clinical evaluations and advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans to precisely identify facet joint pathology. Diagnostic medial branch blocks are often utilized to confirm facet joint involvement by temporarily numbing the nerves supplying these joints. This diagnostic precision allows specialists to tailor treatments ranging from conservative care to minimally invasive procedures like radiofrequency ablation, which disrupts nerve signals and provides longer-lasting relief.
Innovations in Intervention: Beyond Traditional Therapies
When conservative measures fall short, orthopedic treatments that really work include advanced interventions such as facet joint steroid injections and radiofrequency neurotomy. These procedures target inflammation and nerve transmission, offering patients a reprieve from chronic pain. Importantly, patient selection is critical; orthopedic surgeons consider factors like overall spinal alignment and comorbid conditions to maximize outcomes. Understanding these intricacies ensures that treatments are not only effective but also sustainable.
Integrating Holistic Orthopedic Care for Enhanced Recovery
Addressing facet joint pain successfully often involves a multidisciplinary strategy. Incorporating ergonomic education, postural correction, and lifestyle modifications alongside medical treatments helps prevent recurrence. Patients who engage actively in their rehabilitation, including guided orthopedic therapy, experience improved mobility and quality of life. For those interested in exploring comprehensive orthopedic care options for spinal issues, resources such as effective non-surgical care for herniated discs offer valuable insights into complementary approaches.
Ready to take control of your facet joint pain? Share your experiences or questions below to join a community focused on orthopedic health and discover personalized solutions that could transform your daily comfort.
Why Does Facet Joint Pain Feel So Unique and Persistent?
From my own journey and conversations with patients, facet joint pain often stands apart from other back issues due to its localized nature and the way it flares up with certain movements. I remember a patient describing it as a “deep, stabbing sensation” when twisting or extending the spine, which really paints a vivid picture of how this pain interrupts daily life. Unlike diffuse muscular pain, facet joint pain signals a specific structural problem that demands a precise approach rather than generalized remedies.
Personalizing Treatments: What Worked for Me and Others
One thing that struck me in working closely with orthopedic specialists is how treatment plans are shaped not only by imaging results but also by listening deeply to the patient’s story. For example, after an MRI ruled out disc issues, targeted physical therapy focusing on spinal stabilization made a huge difference for me. Strengthening the core and back muscles relieved a significant amount of pressure on the facet joints. I also found that combining this with ergonomic adjustments at work helped prevent flare-ups. If you’re curious about specific exercises or ergonomic tips, check out this guide on orthopedic help for desk workers.
How Can You Tell When It’s Time to Explore Advanced Orthopedic Interventions?
This question often comes up in discussions among those managing facet joint pain. In my experience and according to expert sources like the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, if pain persists beyond a few months despite conservative care, or if it severely limits mobility and quality of life, exploring options like facet joint injections or radiofrequency ablation could be worthwhile. I remember a patient who had tried physical therapy and medication for months but found real relief only after receiving targeted steroid injections, which calmed the inflammation effectively.
Understanding these options and their potential benefits versus risks can empower patients to make informed decisions. For those interested, the detailed insights on effective non-surgical care provide a solid foundation for considering these interventions.
Living with Facet Joint Pain: Encouraging Proactive and Holistic Care
Facet joint pain taught me the value of a multi-pronged strategy—blending medical care, lifestyle changes, and self-awareness. Beyond treatments, adopting mindful movement habits and consistent posture checks throughout the day can make a world of difference. I started keeping a simple daily log to monitor which activities triggered pain and adjusted accordingly, which helped me regain control.
If you’ve faced similar challenges or have tips on managing facet joint pain, I’d love to hear your story. Sharing experiences can build a supportive community and help others find relief. Feel free to comment below or explore more about minimally invasive back pain treatments that might complement your recovery journey.
Cutting-Edge Diagnostic Modalities: Beyond Basic Imaging for Facet Joint Pathology
While MRI and CT scans remain standard tools for detecting facet joint abnormalities, recent advancements have introduced functional imaging techniques that provide deeper insights into joint inflammation and nerve involvement. For instance, Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) combined with CT (SPECT/CT) allows clinicians to localize areas of increased metabolic activity within the facet joints, offering a more precise correlation with symptomatic sites. This fusion imaging helps differentiate between incidental degenerative changes and clinically relevant facet arthropathy, thereby refining treatment targets and avoiding unnecessary interventions.
Additionally, ultrasound-guided diagnostic medial branch blocks have enhanced the accuracy and safety of confirming facet joint pain sources. Real-time visualization ensures precise needle placement while minimizing risks, a critical advancement especially for patients with complex spinal anatomy or previous surgeries.
What Are the Latest Minimally Invasive Orthopedic Procedures Offering Long-Term Relief for Facet Joint Pain?
Emerging minimally invasive techniques have shifted the treatment paradigm for facet joint pain management. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) remains a cornerstone, but innovations such as cooled radiofrequency and bipolar RFA have demonstrated superior lesion size and nerve targeting, translating to prolonged pain relief durations compared to conventional methods.
Furthermore, regenerative medicine approaches are gaining traction. Intra-articular injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or autologous stem cells aim to modulate inflammation and promote tissue repair within the facet joints. Preliminary randomized controlled trials suggest these biologics may reduce pain and improve function, although larger-scale studies are necessary to establish standardized protocols and long-term efficacy (Singh et al., 2021, Journal of Spine Surgery).
Biomechanical Insights: How Spinal Alignment Influences Facet Joint Load and Pain Generation
Understanding the biomechanical context is essential for comprehensive facet joint pain management. Abnormal spinal curvatures—such as hyperlordosis or scoliosis—can disproportionately increase stress on facet joints, accelerating cartilage wear and provoking inflammatory cascades. Advanced gait and posture analyses, coupled with dynamic imaging, help clinicians visualize these mechanical burdens in real time, guiding personalized orthotic and physical therapy interventions that redistribute forces and alleviate painful stimuli.
Moreover, integrating 3D spinal modeling with patient-specific data allows orthopedic surgeons to predict progression patterns of facet degeneration and tailor surgical strategies when indicated. This precision medicine approach is revolutionizing how we anticipate and mitigate chronic facet joint pain complications.
How Do Patient-Specific Factors Influence the Choice Between Conservative and Surgical Facet Joint Treatments?
Decision-making in facet joint pain treatment is multifactorial. Age, comorbidities, pain chronicity, and functional impairment all weigh heavily in selecting an optimal intervention. For example, elderly patients with osteoporosis may be better suited for conservative or minimally invasive procedures to avoid surgical risks, whereas younger patients with focal facet joint osteoarthritis refractory to injections might benefit from surgical fusion or facet joint replacement technologies under development.
Psychosocial factors also play a pivotal role; patients exhibiting central sensitization or chronic pain syndromes may require integrated pain management approaches alongside orthopedic care to achieve meaningful outcomes.
Interested in exploring personalized orthopedic strategies for facet joint pain? Dive deeper into our expert resources or consult with a specialist to craft a treatment plan tailored to your unique biomechanical and clinical profile.
Harnessing Molecular Biomarkers: A New Frontier in Facet Joint Pain Diagnosis
Recent orthopedic research has begun exploring molecular biomarkers present in synovial fluid and serum as potential indicators of facet joint inflammation and degeneration. These biomarkers, including pro-inflammatory cytokines and cartilage degradation products, promise to augment traditional imaging and clinical assessments by providing real-time insights into the biological activity driving pain. Such molecular profiling could soon enable earlier intervention and more precisely tailored therapies, moving beyond symptomatic management to disease modification.
How Can Emerging Biomarker Technologies Revolutionize Personalized Treatment Plans for Facet Joint Pain?
Emerging biomarker assays can stratify patients based on inflammatory profiles and cartilage turnover rates. This stratification allows orthopedic specialists to predict responsiveness to various interventions, from anti-inflammatory pharmacotherapy to regenerative injections. For example, a patient exhibiting elevated interleukin-6 levels might benefit from targeted biologic agents or enhanced anti-inflammatory protocols, while those with predominant cartilage breakdown markers could be candidates for experimental cartilage repair therapies. Integrating biomarker data with advanced imaging and clinical evaluation epitomizes the cutting edge of personalized orthopedic care.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy and Treatment Efficacy
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms in interpreting spinal imaging has significantly improved the detection and grading of facet joint pathology. These technologies analyze complex imaging datasets to identify subtle patterns of degeneration, inflammation, or nerve involvement that might elude human observers. Furthermore, predictive modeling assists clinicians in forecasting disease progression and patient-specific responses to interventions, thus optimizing treatment sequencing and resource allocation.
According to a recent study published in The Spine Journal, AI-assisted diagnostic platforms demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy increase of over 20% in facet joint osteoarthritis detection compared to conventional methods, emphasizing their transformative potential in clinical practice.
Addressing the Psychosocial Dimension: Integrative Approaches for Chronic Facet Joint Pain
Chronic facet joint pain is frequently compounded by psychosocial factors such as anxiety, depression, and pain catastrophizing, which can amplify pain perception and impede recovery. Advanced orthopedic care increasingly incorporates cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness-based stress reduction, and patient education into comprehensive treatment plans. These modalities not only improve coping mechanisms but also facilitate adherence to physical rehabilitation and reduce overall healthcare utilization.
Multidisciplinary pain management teams, integrating orthopedic specialists, psychologists, and physical therapists, exemplify best practices in addressing the biopsychosocial complexity of facet joint pain. This holistic perspective is essential for achieving sustained functional improvements and enhancing quality of life.
Ready to delve into next-generation orthopedic strategies tailored for facet joint pain? Engage with our expert community or schedule a consultation to explore individualized diagnostic and therapeutic innovations designed to restore your mobility and wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What exactly causes facet joint pain and how is it different from other back pain?
Facet joint pain arises from inflammation, degeneration, or injury to the small synovial joints connecting vertebrae. Unlike muscular or disc-related back pain, facet joint pain is typically localized, sharp, and exacerbated by specific spinal movements such as extension or rotation. This distinct pain pattern reflects the joint’s biomechanical role and requires targeted diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
How do orthopedic specialists confirm that facet joints are the source of pain?
Diagnosis involves a combination of detailed clinical examination, advanced imaging modalities like MRI, CT, and functional imaging such as SPECT/CT, and confirmatory diagnostic medial branch nerve blocks. These nerve blocks temporarily numb the nerves supplying the facet joints, and if pain relief occurs, it validates the facet joint as the pain source, enabling precise treatment planning.
What non-surgical treatments are most effective for facet joint pain?
Conservative management includes physical therapy focusing on spinal stabilization, posture correction, ergonomic adjustments, and anti-inflammatory medications. These approaches aim to reduce joint stress, improve mobility, and manage symptoms. Patient engagement and tailored exercise regimens are critical for long-term success.
When should advanced interventions like radiofrequency ablation or steroid injections be considered?
These minimally invasive procedures are indicated when conservative therapies fail to provide adequate relief after several months or when pain significantly impairs function. Radiofrequency ablation disrupts nerve signals to the facet joints for sustained pain control, while steroid injections reduce local inflammation. Patient-specific factors and diagnostic confirmation guide the timing and selection of these interventions.
Are there emerging treatments or technologies that promise better outcomes for facet joint pain?
Yes, regenerative medicine approaches such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell injections are under investigation for their potential to promote tissue healing. Additionally, AI-assisted imaging analysis enhances diagnostic accuracy, and molecular biomarker profiling may soon enable personalized treatment by identifying specific inflammatory or degenerative pathways involved.
How does spinal alignment affect facet joint pain and its management?
Abnormal spinal curvatures like scoliosis or hyperlordosis increase mechanical loading on facet joints, accelerating degeneration and pain. Understanding these biomechanical influences allows orthopedic specialists to customize interventions such as orthotic support and targeted physical therapy to redistribute forces and alleviate symptoms.
Can psychosocial factors influence the experience and treatment of facet joint pain?
Absolutely. Anxiety, depression, and pain catastrophizing can amplify pain perception and hinder recovery. Integrating cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness, and patient education into treatment plans helps address these factors, improving coping strategies and adherence to rehabilitation.
What role does patient lifestyle play in preventing and managing facet joint pain?
Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining an active routine, practicing ergonomic postures, avoiding prolonged static positions, and managing weight are essential components. Patients who actively participate in their care and adopt mindful movement habits generally experience better outcomes and reduced recurrence.
Is surgery commonly required for facet joint pain?
Surgery is typically reserved for cases where severe facet joint degeneration causes spinal instability or nerve compression unresponsive to conservative and minimally invasive treatments. Surgical options include fusion or emerging facet joint replacement techniques, chosen based on individual patient factors and biomechanical considerations.
How can patients best navigate treatment decisions for facet joint pain?
Engaging with orthopedic specialists who employ a comprehensive diagnostic approach including advanced imaging, biomarker analysis, and consideration of psychosocial factors ensures personalized care. Patients should communicate openly about symptoms, treatment preferences, and lifestyle to collaboratively develop an optimal management plan.
Trusted External Sources
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS): Provides evidence-based clinical guidelines and patient resources specific to spinal and facet joint conditions, ensuring authoritative treatment recommendations.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI): A repository of peer-reviewed biomedical research, including studies on facet joint pathology, diagnostic techniques, and emerging therapies.
- The Spine Journal: A leading specialized publication offering cutting-edge research on spinal disorders, including AI applications and regenerative medicine advances relevant to facet joint pain.
- Journal of Spine Surgery: Publishes clinical trials and reviews focused on innovative surgical and minimally invasive treatments for facet joint and other spinal disorders.
- International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine (ISSLS): Offers expert consensus and biomechanical research critical for understanding facet joint load dynamics and treatment implications.
Conclusion
Facet joint pain represents a distinct and multifaceted clinical challenge that demands precision in diagnosis and personalization in treatment. From advanced imaging and molecular biomarkers to innovative minimally invasive interventions, orthopedic care has evolved to offer targeted relief while addressing biomechanical and psychosocial dimensions. Integrating conservative therapies with cutting-edge technologies and holistic strategies empowers patients to reclaim mobility and quality of life. By understanding the complex interplay of factors driving facet joint pain, individuals and clinicians can collaborate effectively to devise sustainable solutions. Explore further expert insights, share your experiences, or consult with orthopedic specialists to embark on a tailored path toward pain resolution and spinal health restoration.

I’ve dealt with facet joint pain for a while, and reading about how this pain differs from general back pain really resonated with me. The sharp, localized nature coupled with stiffness definitely made daily activities challenging, especially when the pain flared up during specific movements like twisting or bending backward. What stood out to me was the emphasis on precision in diagnosis—particularly the use of diagnostic medial branch blocks. Before, I was only familiar with MRI scans, but understanding how nerve blocks can confirm the exact source of pain helps explain why some treatments may or may not work. I also appreciate the focus on non-surgical options like targeted physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve flexibility, as I’ve seen real benefits after consistent therapy sessions tailored to my needs. However, I’m curious about how different patients respond to the combination of ergonomic adjustments and physical therapy, especially those who have desk jobs or sedentary lifestyles. For others managing facet joint pain, what lifestyle habits or specific exercises have you found most effective in preventing flare-ups? It would be great to share practical tips that can complement medical treatments and improve daily comfort.
This post really highlights how important precision is in managing facet joint pain. I’ve personally found that combining physical therapy with ergonomic changes makes a significant difference in the long run. Especially working at a desk; I’ve started using a sit-stand desk and making sure my monitor is at eye level to reduce strain. I’m curious, has anyone else had success integrating specific posture adjustments or ergonomic tools into their routine? Additionally, I wonder how the use of advanced imaging, like SPECT/CT or ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, has improved treatment accuracy for others. For me, strengthening core muscles has been crucial, but I’d love to hear what other practical exercises or habits have helped fellow readers prevent flare-ups. Sometimes, making small daily tweaks can be surprisingly effective in managing symptoms and avoiding invasive procedures. Thanks for sharing such a comprehensive overview—it’s inspiring to see how evolving technology and personalized care are paving the way for more sustainable treatment options.