Unlocking Shoulder Healing: The Power of Orthopedic Rehab for Rotator Cuff Tears
A rotator cuff tear can feel like a sudden betrayal of your shoulder’s strength, disrupting daily tasks and athletic pursuits alike. But with the right orthopedic rehab exercises, recovery is not only possible — it can also be empowering. These exercises help restore mobility, rebuild strength, and reduce pain, setting a foundation for lasting shoulder health.
Targeted Movements: Why Specific Exercises Matter in Rotator Cuff Rehab
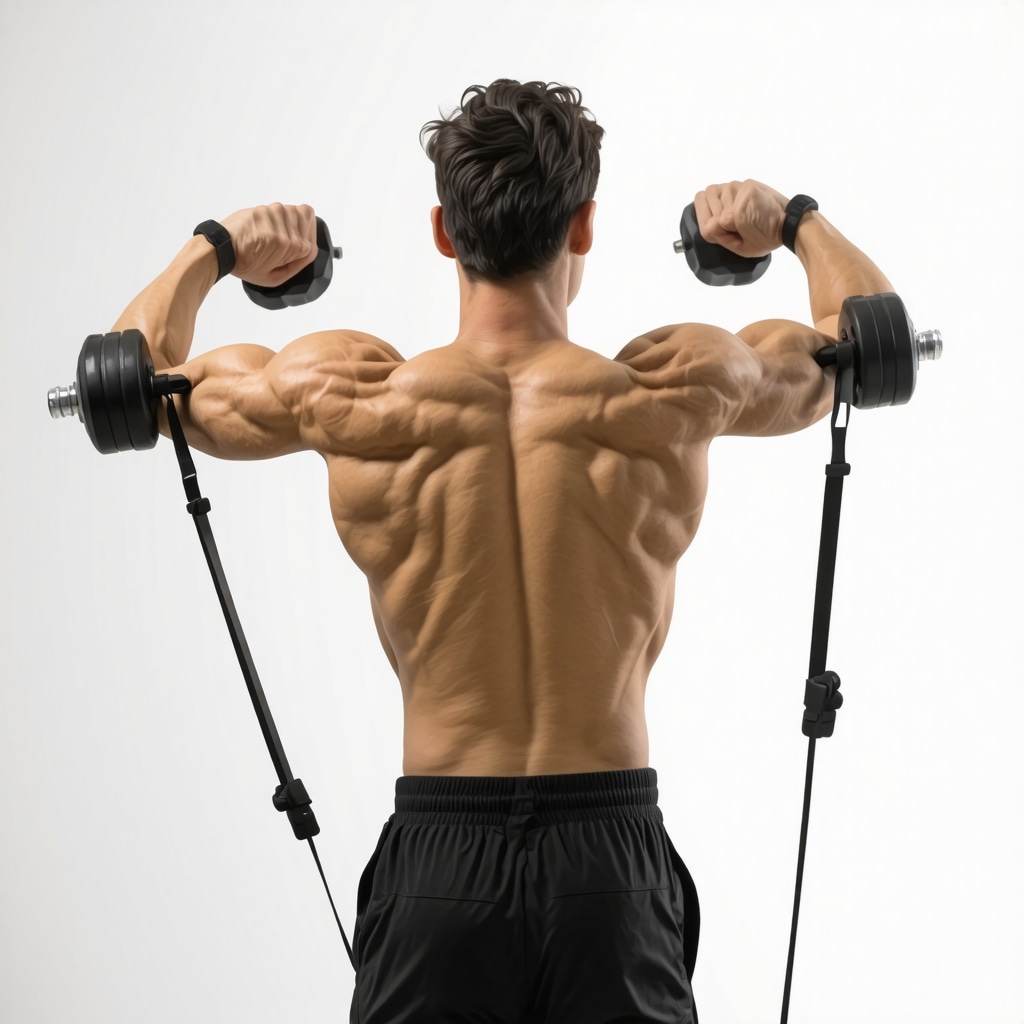
Not all exercises are created equal when it comes to healing a rotator cuff tear. Effective rehab focuses on controlled, progressive movements that gently engage the four muscles making up the rotator cuff: supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. For instance, isometric holds can activate these muscles without aggravating the injury, while dynamic exercises like external rotation with resistance bands promote muscle balance and joint stability.
How Do Orthopedic Specialists Determine the Best Rehab Exercises for Rotator Cuff Tears?
Orthopedic experts tailor rehab programs based on tear severity, patient age, activity level, and pain tolerance. Initial phases emphasize pain control and gentle range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness. As healing progresses, strengthening and endurance exercises are introduced cautiously. This nuanced approach is critical; overexertion risks worsening the tear, while underuse may cause muscle atrophy. Expert evaluation often includes physical assessments and imaging to guide precise exercise prescription. Comprehensive guidance such as the recommendations from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons underscores the importance of individualized rehab plans (AAOS Rotator Cuff Tear Guidelines).
Orthopedic Rehab Essentials: 3 Effective Exercises to Incorporate
1. Pendulum Swings: Lean forward, letting your arm dangle freely. Gently swing it in small circular motions to promote joint lubrication and reduce stiffness without muscle strain.
2. External Rotation with Resistance Band: Attach a resistance band to a stable surface, keep your elbow at your side bent 90 degrees, and rotate your forearm outward slowly. This strengthens the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles crucial for shoulder stability.
3. Scapular Retraction: Sit or stand upright and squeeze your shoulder blades together, holding for a few seconds. This exercise enhances scapular stability, which supports rotator cuff recovery and prevents compensatory injuries.
Insights from Experience: Real-World Rehab Success
Consider the case of a 45-year-old avid tennis player who sustained a partial rotator cuff tear. Under expert orthopedic care, she began a structured rehab routine emphasizing slow progression and exercise variety. Over 12 weeks, her pain diminished significantly, range of motion improved, and she safely returned to play. This practical example illustrates how adherence to a carefully designed exercise protocol, combined with professional monitoring, can transform recovery outcomes.
Explore More Orthopedic Solutions for Shoulder and Spine Health
Understanding how to effectively rehabilitate a rotator cuff tear is a vital step in orthopedic care. For those interested in broader musculoskeletal health, including spine injury treatments and non-surgical options, valuable resources are available such as this comprehensive orthopedic guide on rotator cuff tear treatments. Engaging with expert orthopedic advice ensures your recovery journey is well-informed and tailored to your needs.
If you found these insights helpful, please consider sharing your thoughts or experiences in the comments below. Sharing knowledge empowers others facing similar challenges and fosters a supportive healing community.
Listening to Your Body: The Journey Beyond Basic Exercises
When I first started my orthopedic rehab for a rotator cuff tear, I quickly realized it wasn’t just about doing the exercises; it was about tuning into how my shoulder responded. Each day presented different challenges—some days the pain was sharper, other days I felt hopeful progress. This personal experience taught me that patience and mindfulness are just as important as the exercises themselves.
For instance, on days when I felt increased discomfort, I scaled back the intensity, focusing on gentle pendulum swings and scapular retractions. On better days, gradually increasing the resistance during external rotation exercises helped rebuild strength while respecting the healing process. This adaptive approach prevented setbacks and fostered consistent improvement.
Incorporating Orthopedic Rehab Into Daily Life: Practical Tips
One of the biggest hurdles in recovery is integrating rehab into a busy routine. Early on, I scheduled short sessions morning and evening, making exercises manageable and less daunting. Keeping resistance bands and instructional guides handy in my living space reminded me to stay consistent.
Moreover, I learned to combine rehab with lifestyle adjustments, such as improving my posture during desk work to avoid additional strain on my shoulder. For others facing similar issues, resources like orthopedic care tips for desk workers can be invaluable in preventing chronic pain while supporting recovery.
Ever Wondered How Long It Really Takes to Heal a Rotator Cuff Tear?
Healing times vary widely depending on tear size, treatment method, and individual health factors. Based on my own experience and discussions with my orthopedic specialist, small partial tears may improve significantly within 6 to 12 weeks with dedicated rehab, while more severe tears might require months or even surgical intervention followed by extended rehab.
It’s important to remember, as highlighted by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, that consistent and progressive exercise adherence combined with professional guidance is key to optimal recovery timelines.
Why Professional Guidance Makes a Difference
While I found many exercises online, working with an orthopedic therapist helped tailor the plan to my unique needs. They monitored my progress, modified exercises to avoid compensatory movements, and provided hands-on techniques that accelerated healing.
If you’re navigating a similar journey, consider consulting specialists who can offer personalized treatment. You might explore options like choosing the right orthopedic surgeon or non-surgical care alternatives discussed in non-surgical orthopedic care guides.
Have you experienced orthopedic rehab or are you currently on a recovery path? Share your story or questions below—your insights could be the encouragement someone else needs. Let’s keep the conversation going and support each other through these challenges.
Integrative Approaches: Leveraging Neuromuscular Re-education in Rotator Cuff Rehab
Beyond traditional strengthening exercises, incorporating neuromuscular re-education can dramatically improve shoulder function after a rotator cuff tear. This advanced strategy focuses on retraining the brain and muscles to work harmoniously, restoring proper movement patterns and preventing compensatory mechanics that can lead to chronic pain or re-injury. Techniques such as biofeedback, proprioceptive training, and functional movement drills are essential components of this approach. For example, targeted closed-chain exercises on unstable surfaces help improve joint position sense and dynamic stability, which are critical for athletes and active individuals.
Neuromuscular re-education also addresses the often-overlooked scapulothoracic rhythm — the coordinated movement between the scapula and humerus. Disruptions here can perpetuate rotator cuff dysfunction even after the tear heals. Orthopedic specialists commonly integrate exercises emphasizing scapular upward rotation and posterior tilt to restore this delicate balance. This nuanced rehabilitation phase requires precise monitoring and progression to optimize outcomes.
What Role Does Proprioception Play in Long-Term Rotator Cuff Repair Success?
Proprioception, the body’s ability to sense joint position and movement, is fundamental in preventing further injury and ensuring functional recovery. After a rotator cuff tear, proprioceptive deficits often persist, leading to altered biomechanics and increased risk of future tears or shoulder instability. Incorporating proprioceptive training into rehab—such as using wobble boards, balance balls, or dynamic weight-bearing activities—enhances neuromuscular control. A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma demonstrated that patients engaging in proprioceptive-focused rehab protocols exhibited faster return to activity and reduced re-injury rates compared to standard strengthening programs.
Understanding and integrating proprioceptive elements thus represent a sophisticated layer in rotator cuff rehab, moving beyond mere muscle strengthening toward holistic functional restoration.
Advanced Modalities: Complementing Exercise with Cutting-Edge Orthopedic Technologies
Modern orthopedic rehabilitation increasingly employs adjunctive technologies to augment exercise benefits for rotator cuff tears. Modalities such as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections have shown promise in promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation. While these treatments are not standalone cures, when combined with targeted rehab exercises, they can accelerate recovery and improve patient outcomes.
For instance, LLLT utilizes specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular metabolism and collagen synthesis within the injured rotator cuff tendons. ESWT delivers mechanical pulses that enhance blood flow and tissue regeneration. Meanwhile, PRP injections provide concentrated growth factors directly to the injury site, potentially enhancing the body’s natural healing cascade. These therapies must be prescribed judiciously by orthopedic specialists, considering patient-specific factors and evidence-based protocols.
Integrating Psychological Resilience: The Overlooked Pillar in Orthopedic Rehab
Physical recovery from a rotator cuff tear is intimately linked with psychological resilience. Chronic pain, functional limitations, and fear of re-injury often contribute to anxiety and decreased motivation, which can hinder adherence to rehab regimens. Incorporating cognitive-behavioral strategies, mindfulness, and patient education into the rehab process fosters mental well-being and empowers patients to engage actively in their recovery journey.
Orthopedic rehabilitation teams increasingly collaborate with psychologists and pain specialists to address these psychosocial aspects. Such integrative care models underscore that successful rotator cuff recovery is multifaceted, extending beyond biomechanics to encompass emotional and cognitive health.
If you’re navigating the complexities of rotator cuff rehab or looking to optimize your recovery with advanced strategies, consult with an orthopedic specialist who can tailor a comprehensive program blending these cutting-edge approaches. Explore in-depth guides and connect with professionals through advanced rotator cuff rehabilitation resources to elevate your healing journey.
Precision in Progression: Tailoring Load Management for Optimal Tendon Healing
Advanced orthopedic rehabilitation for rotator cuff tears transcends basic exercise paradigms by incorporating meticulous load management strategies. Progressive loading protocols are calibrated not only to stimulate tendon remodeling but also to avoid deleterious overstrain that could exacerbate tendon degeneration. Utilizing tools such as isokinetic dynamometry and wearable motion sensors, clinicians can quantitatively monitor shoulder kinetics and adapt exercise intensity dynamically, fostering an environment conducive to collagen realignment and tensile strength restoration.
Synergistic Rehabilitation: Combining Manual Therapy with Targeted Neuromuscular Control
Integrating manual therapy techniques—such as myofascial release and joint mobilizations—with neuromuscular re-education enhances proprioceptive acuity and neuromotor efficiency. Such synergy mitigates compensatory movement patterns and facilitates optimal scapulohumeral rhythm. This multifaceted approach aligns with findings published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, which highlights improved functional outcomes when manual interventions complement neuromotor training in rotator cuff rehabilitation.
How Can Emerging Biomechanical Assessment Technologies Revolutionize Personalized Rotator Cuff Rehab?
Emerging biomechanical assessment technologies, including three-dimensional motion capture and surface electromyography (sEMG), enable unparalleled precision in evaluating muscle activation patterns and joint kinematics during rehabilitation exercises. These insights facilitate bespoke rehab protocols that address individual neuromuscular deficits and asymmetries, thereby optimizing therapeutic efficacy. By capturing subtle aberrations in movement early, clinicians can preempt maladaptive strategies that often underlie persistent dysfunction and re-injury.
Such advanced diagnostics are increasingly accessible in specialized orthopedic centers and represent a frontier in personalized medicine for musculoskeletal injuries.
Integrating Lifestyle Medicine: The Role of Nutrition and Sleep in Tendon Regeneration
Beyond mechanical and neuromuscular interventions, adjunctive lifestyle modifications notably influence rotator cuff healing trajectories. Nutritional strategies emphasizing anti-inflammatory micronutrients—such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, and collagen peptides—support tendon extracellular matrix synthesis and modulate oxidative stress. Likewise, optimizing sleep quality enhances growth hormone secretion and tissue repair processes, underscoring the interdependence of physiological systems in musculoskeletal recovery.
Clinicians increasingly advocate for holistic patient education encompassing these dimensions to maximize functional restoration and minimize chronicity.
Empowering Patients Through Tele-Rehabilitation: Expanding Access to Specialized Care
Tele-rehabilitation platforms offer innovative solutions to bridge geographic and resource barriers, delivering expert-guided rotator cuff rehab remotely. Leveraging real-time video consultations, digital exercise monitoring, and patient-reported outcome measures, these programs maintain adherence and enable timely adjustments to therapy plans. This modality is particularly beneficial in the context of ongoing global health challenges or for patients with mobility constraints, ensuring continuity of specialized orthopedic care.
Clinicians adopting tele-rehabilitation protocols report enhanced patient engagement and comparable outcomes to traditional in-person therapy, heralding a paradigm shift in musculoskeletal rehabilitation delivery.
If you are committed to advancing your rotator cuff recovery with cutting-edge, evidence-based strategies, consider consulting with an orthopedic specialist experienced in integrating these innovative modalities. Engage with our community by sharing your questions or insights—your participation enriches collective expertise and supports progressive healing journeys.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the typical timeline for healing a rotator cuff tear with orthopedic rehab?
Healing timelines vary based on tear severity, patient health, and rehabilitation adherence. Small partial tears often show significant improvement within 6 to 12 weeks of consistent rehab, while larger or full-thickness tears may require several months and sometimes surgical intervention followed by extended rehab. Continuous professional monitoring ensures progression aligns with tissue healing.
How do orthopedic specialists customize rehab exercises for individual patients?
Customization involves assessing tear size, patient age, activity demands, pain levels, and imaging findings. Specialists begin with pain management and gentle range-of-motion exercises, then progressively introduce strengthening and neuromuscular training tailored to the patient’s specific functional goals and healing status, minimizing risks of overuse or compensatory injuries.
Why is neuromuscular re-education important in rotator cuff rehabilitation?
Neuromuscular re-education retrains the brain-muscle connection to restore proper movement patterns and scapulothoracic rhythm. It enhances proprioception, prevents compensatory mechanics, and reduces re-injury risk by improving dynamic shoulder stability, which is critical for long-term functional recovery beyond mere muscle strengthening.
What role do advanced technologies like low-level laser therapy and PRP play in recovery?
These modalities serve as adjuncts to exercise-based rehab by promoting tissue healing, reducing inflammation, and stimulating collagen synthesis. Low-level laser therapy and extracorporeal shockwave therapy enhance cellular metabolism and blood flow, while platelet-rich plasma injections deliver growth factors to the injury site. Their use is evidence-based and carefully integrated by orthopedic professionals.
How can psychological resilience influence orthopedic rehab outcomes?
Psychological factors such as motivation, anxiety, and fear of re-injury can significantly impact adherence and recovery progress. Incorporating cognitive-behavioral techniques, mindfulness, and patient education supports mental well-being, which helps patients stay engaged and overcome challenges during the rehab process, enhancing overall outcomes.
Are tele-rehabilitation programs effective for rotator cuff injury recovery?
Yes, tele-rehabilitation offers accessible, expert-guided rehab through real-time video, exercise monitoring, and patient feedback. Studies show comparable results to in-person therapy, making it a valuable option for patients with geographic, mobility, or scheduling constraints, ensuring continuity of specialized orthopedic care.
What lifestyle factors support tendon regeneration during rotator cuff rehab?
Nutrition rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, and collagen peptides supports tendon repair. Adequate sleep is also essential as it facilitates hormonal regulation and tissue regeneration. Orthopedic rehab is most effective when combined with such holistic lifestyle modifications.
How do biomechanical assessment technologies enhance personalized rehab plans?
Tools like 3D motion capture and surface electromyography provide detailed insights into muscle activation and joint kinematics. These data allow clinicians to identify dysfunctional movement patterns precisely and tailor exercises that address individual neuromuscular deficits, optimizing therapeutic effectiveness and preventing re-injury.
Can manual therapy improve outcomes when combined with neuromuscular training?
Integrating manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations and myofascial release with neuromuscular re-education improves proprioceptive feedback and neuromotor control. This combined approach enhances scapulohumeral rhythm and functional recovery, reducing compensatory patterns and pain.
How important is load management in rotator cuff tendon healing?
Careful load management is critical to stimulate tendon remodeling without causing overload or re-injury. Progressive, quantitatively monitored loading protocols ensure collagen realignment and tendon strength restoration, balancing therapeutic benefit with tissue protection throughout rehab.
Trusted External Sources
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS): Provides authoritative clinical guidelines and evidence-based recommendations for rotator cuff tear treatment and rehab, ensuring safe and effective care protocols.
- Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy: Publishes rigorous research on rehabilitation techniques, including the integration of manual therapy and neuromuscular training for shoulder injuries.
- Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma: Offers peer-reviewed studies on proprioceptive training and functional recovery strategies relevant to rotator cuff injury rehabilitation.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – MedlinePlus: Delivers comprehensive, patient-friendly information on rotator cuff disorders, healing processes, and therapeutic options.
- Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research (CORR): Features advanced research on orthopedic surgical and non-surgical interventions, including emerging technologies in tendon healing.
Conclusion
Orthopedic rehabilitation for rotator cuff tears is a multifaceted journey that extends well beyond basic strengthening exercises. By integrating tailored exercise protocols, neuromuscular re-education, advanced adjunctive therapies, and lifestyle modifications, patients can achieve meaningful pain relief, functional restoration, and reduced re-injury risk. Psychological resilience and emerging technologies further empower personalized, effective recovery pathways. Whether recovering from a partial tear or navigating complex cases, collaboration with orthopedic specialists ensures a comprehensive and adaptive rehab plan. Embrace the insights and strategies shared here to optimize your shoulder health—engage actively, stay informed, and consider sharing your experiences to support others on similar paths toward recovery and well-being.


I found the emphasis on individualized orthopedic rehab for rotator cuff tears really insightful. In my experience, the journey to recovery is rarely linear—what worked well early on sometimes had to be adjusted as my shoulder felt different over time. I particularly appreciated the mention of isometric exercises and gentle pendulum swings; these helped me maintain joint mobility without exacerbating pain during the initial healing phase. It’s interesting how the article highlights the importance of balancing strengthening with careful load management to avoid setbacks. I’ve personally struggled with pushing too hard too soon, which led to frustration and longer recovery periods. Has anyone else found that integrating neuromuscular re-education and proprioceptive training made a tangible difference in regaining confidence and functional movement? I’ve heard these can be game changers but haven’t tried them extensively yet. Also, adopting a mindful approach by listening to your body’s signals, as mentioned here, seems crucial—something I wish I embraced earlier. I’m curious about others’ strategies for blending professional guidance with self-awareness during rehab, especially when juggling busy schedules or lifestyle commitments. Any practical tips or experiences would be appreciated!
The post offers a comprehensive view of the rehab process, and I especially appreciate the emphasis on listening to your body during recovery. During my own shoulder rehab after a tear, I found that the most progress came when I paid close attention to how each movement affected my shoulder’s response. It’s easy to push through discomfort, but knowing when to back off is crucial. I wonder, how do others balance the need for consistent rehab exercises with the risk of overexertion, especially when motivation wanes? I also found that incorporating mindful breathing techniques helped me stay centered and avoid rushing the process, which can sometimes lead to setbacks. Personally, I’ve seen significant benefits from adding proprioceptive exercises like balancing on unstable surfaces, which improved my confidence in moving without fear of re-injury. Have others experienced a noticeable difference with neuromuscular re-education, and if so, how did they integrate it into daily routines? It seems like a vital component for long-term shoulder stability.