Unlocking the Mystery: Why Early Orthopedic Consultation Matters for Rotator Cuff Tears
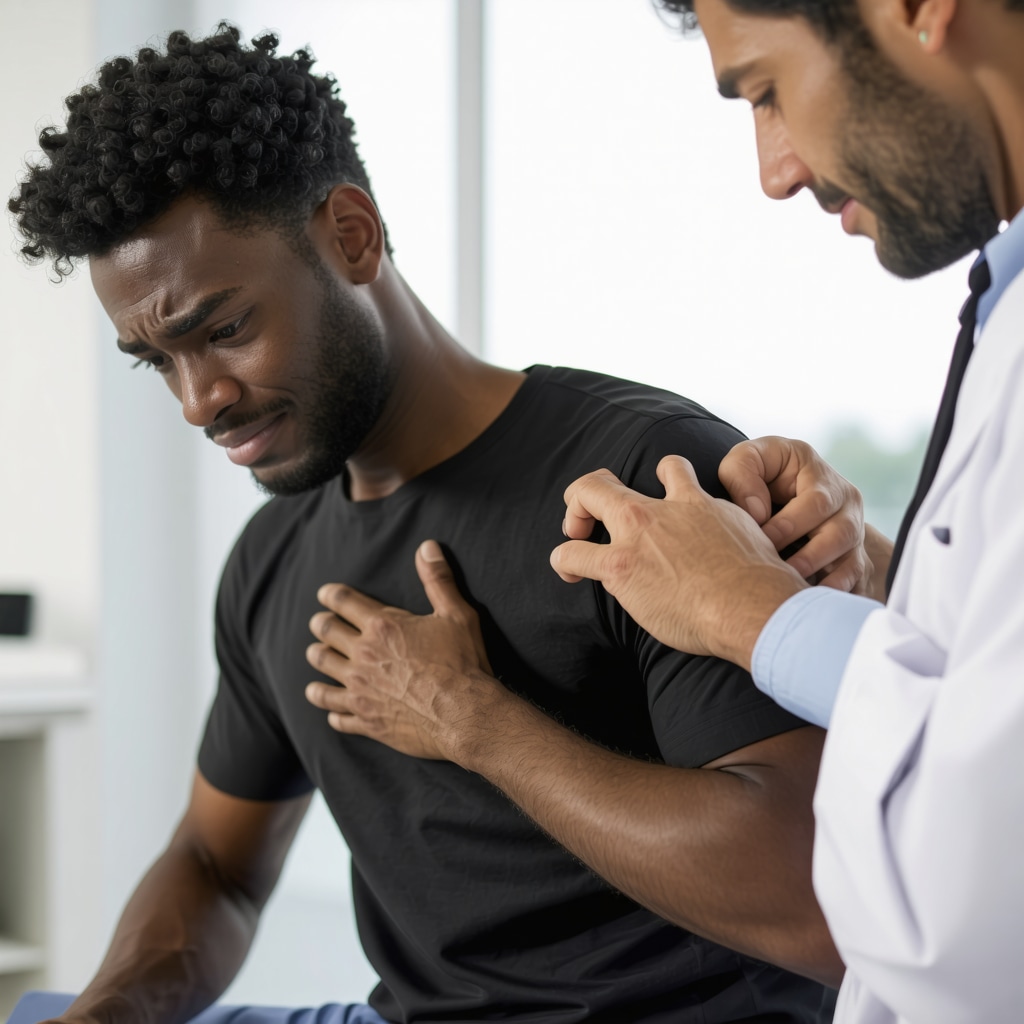
Rotator cuff tears are a common yet often underestimated cause of shoulder pain and dysfunction. Many individuals delay seeking professional help, mistaking discomfort for a minor strain or overuse injury. However, timely evaluation by an orthopedic doctor can profoundly influence recovery outcomes. Understanding when to seek expert care is essential to preserve shoulder mobility and prevent chronic complications.
Spotting the Silent Signals: Subtle Symptoms That Demand Attention
Not all rotator cuff tears announce themselves with dramatic pain. Sometimes, patients experience a nagging ache, weakness when lifting the arm, or difficulty performing routine tasks such as combing hair or reaching behind the back. These subtle signs often precede full tears and can indicate partial tendon damage. If these symptoms persist beyond a few weeks despite rest and home remedies, consulting an orthopedic specialist becomes imperative.
When Does Shoulder Pain Cross the Threshold for Orthopedic Intervention?
How can you tell if your rotator cuff injury requires professional orthopedic evaluation?
Persistent pain lasting more than 6 weeks, especially if accompanied by significant weakness or limited range of motion, often signals the need for an orthopedic assessment. Acute injuries with sudden sharp pain, swelling, or a popping sensation during activities like lifting heavy objects or sports also warrant immediate attention. An orthopedic doctor will perform a detailed clinical examination and may order imaging studies such as MRI or ultrasound to accurately diagnose the extent of tendon damage.
Beyond Pain Relief: The Orthopedic Doctor’s Role in Tailored Rotator Cuff Management
Orthopedic specialists bring a wealth of expertise in both nonsurgical and surgical treatment options. For many patients, targeted physical therapy and anti-inflammatory measures can restore function effectively. However, when conservative care fails or tears are extensive, surgical repair may be necessary to reattach or reconstruct the torn tendon. Orthopedic doctors also guide patients through post-treatment rehabilitation protocols designed to optimize healing and prevent re-injury.
Learning from Experience: A Case Study in Timely Orthopedic Care
Consider the example of a middle-aged athlete who ignored intermittent shoulder discomfort for months. Eventually, he experienced substantial weakness and inability to perform overhead activities. After seeking orthopedic evaluation, an MRI revealed a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. Early surgical intervention followed by structured rehabilitation enabled him to regain near-normal function within six months, underscoring the value of prompt expert care.
For those interested in a deeper dive into rotator cuff tear treatments and when to escalate care, visit Choosing an Orthopedic Doctor for Rotator Cuff Tear Treatment.
Shoulder health is vital for everyday quality of life. If you or a loved one experiences persistent shoulder pain or weakness, consider consulting an orthopedic doctor sooner rather than later to explore effective treatment avenues.
Have you encountered shoulder pain that lingered longer than expected? Share your experience or questions below to help others navigate the path to recovery.
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve outcomes for rotator cuff injuries (AAOS Rotator Cuff Tear Info).
Reflecting on Recovery: The Journey Beyond Surgery
After witnessing friends and family go through rotator cuff tear treatments, I’ve come to appreciate how recovery isn’t just about the procedure itself. It’s about the patience and perseverance that follow. One close friend underwent surgery after months of neglecting his shoulder pain. The surgery was successful, but the true challenge lay in the rehabilitation phase. The orthopedic team emphasized a gradual approach, combining physical therapy with mindful daily activity adjustments. This experience showed me that orthopedic care extends far beyond the operating room, focusing on restoring quality of life.
Adapting Lifestyle: Small Changes, Big Impact
In conversations with patients and orthopedic professionals, I learned how small lifestyle modifications can significantly ease rotator cuff strain. For instance, ergonomic adjustments at work—especially if you’re a desk worker—can prevent undue stress on your shoulder. Simple shifts like adjusting chair height or using supportive braces can make a difference. If you spend long hours at a desk, check out resources on orthopedic help for desk workers that offer practical tips to protect your spine and shoulders.
When Should You Consider Surgery? A Personal Take
One question I hear often is, “How do I know if surgery is my best option?” From stories and expert advice, it boils down to the severity of the tear and how much it impacts your daily function. If pain and weakness persist despite conservative measures like physical therapy and medication, surgery often becomes the next step. An orthopedic surgeon can guide you through this decision, explaining risks and benefits tailored to your condition. For detailed guidance, I recommend reading about choosing the right orthopedic surgeon to ensure you find someone who understands your unique needs.
Could Early Orthopedic Care Prevent the Need for Surgery?
This question has intrigued me, especially after learning from the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons that early intervention can often halt progression and improve outcomes. It’s fascinating to consider that prompt consultation might help avoid invasive procedures altogether. Has anyone here experienced a rotator cuff injury they managed successfully without surgery due to early orthopedic care? Your stories could inspire others to seek help sooner.
Sharing and Learning Together
Shoulder pain can be isolating, but sharing our journeys helps build a community of support. Have you had experiences with rotator cuff tear treatment—whether surgical or nonsurgical—that shaped your outlook? Or perhaps tips on managing daily activities while healing? I invite you to leave comments below and share your insights. If you want to explore more about orthopedic treatments and recovery strategies, check out our orthopedic rehab tips that also touch on general recovery principles applicable to shoulder injuries.
Decoding Complex Rotator Cuff Tears: Multidimensional Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
Rotator cuff tears are not monolithic; they vary widely in size, location, and chronicity, which complicates both diagnosis and management. Complex tears may involve multiple tendons, retraction of the torn edges, or significant muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration. These factors critically influence prognosis and require sophisticated imaging interpretation—often going beyond standard MRI to include dynamic ultrasound or even 3D MRI reconstructions for surgical planning.
Orthopedic surgeons specializing in shoulder pathology emphasize that understanding the biomechanical impact of these tears is pivotal. The rotator cuff’s primary role in stabilizing the glenohumeral joint means that untreated complex tears can lead to secondary degenerative joint changes, such as cuff tear arthropathy. This underscores the importance of a nuanced, patient-specific approach rather than one-size-fits-all treatment.
What are the latest advancements in surgical techniques for massive or irreparable rotator cuff tears?
Emerging surgical options for massive or irreparable tears include superior capsular reconstruction (SCR), tendon transfers, and biologic augmentations using scaffolds or growth factors. SCR aims to restore the superior stability of the shoulder by reconstructing the capsule, thereby improving function and reducing pain. Tendon transfers, such as latissimus dorsi or pectoralis major transfers, compensate for lost rotator cuff function by redirecting muscle forces.
Biologic augmentation with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or stem cell therapies is under active investigation to enhance tendon healing quality and reduce retear rates. However, these approaches require careful patient selection and remain adjuncts rather than replacements for mechanical repair. Current evidence from randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses is shaping consensus on best practices, but the field continues to evolve rapidly (J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020; Biologic Augmentation in Rotator Cuff Repair).
Integrating Rehabilitation Science: Tailored Postoperative Protocols for Optimal Recovery
Postoperative rehabilitation is equally critical in determining long-term outcomes. Advanced protocols now emphasize graduated loading based on tendon healing biology and individual patient factors such as age, tear chronicity, and comorbidities. Early passive motion may be beneficial for some, while others require prolonged immobilization to protect repair integrity.
Orthopedic rehabilitation specialists often employ neuromuscular re-education to restore proprioception and dynamic joint stability, which are vital for preventing recurrent injury. Emerging technologies like biofeedback and virtual reality-assisted therapy are being explored to enhance patient engagement and functional gains.
Patient-Centered Decision Making: Balancing Risks, Benefits, and Expectations
Complex rotator cuff pathology demands a shared decision-making framework. Patients benefit from understanding the spectrum of options—from conservative management to cutting-edge surgical interventions—and their realistic outcomes. Orthopedic specialists provide individualized risk assessments considering factors such as smoking, diabetes, and activity level that influence healing potential.
Open dialogue about potential complications, including stiffness, retear, and persistent pain, fosters informed consent and aligns treatment goals. Multidisciplinary collaboration with physical therapists, pain management experts, and sometimes psychologists can holistically support recovery.
Are you navigating a complex rotator cuff tear diagnosis or considering advanced treatment options? Connect with our orthopedic experts for personalized evaluation and cutting-edge care strategies tailored to your unique condition.
Decoding Complex Rotator Cuff Tears: Multidimensional Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
Rotator cuff tears are not monolithic; they vary widely in size, location, and chronicity, which complicates both diagnosis and management. Complex tears may involve multiple tendons, retraction of the torn edges, or significant muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration. These factors critically influence prognosis and require sophisticated imaging interpretation—often going beyond standard MRI to include dynamic ultrasound or even 3D MRI reconstructions for surgical planning.
Orthopedic surgeons specializing in shoulder pathology emphasize that understanding the biomechanical impact of these tears is pivotal. The rotator cuff’s primary role in stabilizing the glenohumeral joint means that untreated complex tears can lead to secondary degenerative joint changes, such as cuff tear arthropathy. This underscores the importance of a nuanced, patient-specific approach rather than one-size-fits-all treatment.
What are the latest advancements in surgical techniques for massive or irreparable rotator cuff tears?
Emerging surgical options for massive or irreparable tears include superior capsular reconstruction (SCR), tendon transfers, and biologic augmentations using scaffolds or growth factors. SCR aims to restore the superior stability of the shoulder by reconstructing the capsule, thereby improving function and reducing pain. Tendon transfers, such as latissimus dorsi or pectoralis major transfers, compensate for lost rotator cuff function by redirecting muscle forces.
Biologic augmentation with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or stem cell therapies is under active investigation to enhance tendon healing quality and reduce retear rates. However, these approaches require careful patient selection and remain adjuncts rather than replacements for mechanical repair. Current evidence from randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses is shaping consensus on best practices, but the field continues to evolve rapidly (J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020; Biologic Augmentation in Rotator Cuff Repair).
Integrating Rehabilitation Science: Tailored Postoperative Protocols for Optimal Recovery
Postoperative rehabilitation is equally critical in determining long-term outcomes. Advanced protocols now emphasize graduated loading based on tendon healing biology and individual patient factors such as age, tear chronicity, and comorbidities. Early passive motion may be beneficial for some, while others require prolonged immobilization to protect repair integrity.
Orthopedic rehabilitation specialists often employ neuromuscular re-education to restore proprioception and dynamic joint stability, which are vital for preventing recurrent injury. Emerging technologies like biofeedback and virtual reality-assisted therapy are being explored to enhance patient engagement and functional gains.
Patient-Centered Decision Making: Balancing Risks, Benefits, and Expectations
Complex rotator cuff pathology demands a shared decision-making framework. Patients benefit from understanding the spectrum of options—from conservative management to cutting-edge surgical interventions—and their realistic outcomes. Orthopedic specialists provide individualized risk assessments considering factors such as smoking, diabetes, and activity level that influence healing potential.
Open dialogue about potential complications, including stiffness, retear, and persistent pain, fosters informed consent and aligns treatment goals. Multidisciplinary collaboration with physical therapists, pain management experts, and sometimes psychologists can holistically support recovery.
Are you navigating a complex rotator cuff tear diagnosis or considering advanced treatment options? Connect with our orthopedic experts for personalized evaluation and cutting-edge care strategies tailored to your unique condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the early signs of a rotator cuff tear that should prompt an orthopedic consultation?
Early signs include persistent shoulder pain lasting more than six weeks, weakness during lifting or overhead activities, limited range of motion, and difficulty performing daily tasks like reaching behind the back or combing hair. Subtle symptoms such as a nagging ache or intermittent discomfort should not be ignored, especially if they persist despite rest and home remedies. Prompt orthopedic evaluation helps prevent progression to full-thickness tears and chronic dysfunction.
Can all rotator cuff tears be treated non-surgically?
Not all tears require surgery. Many partial or small tears respond well to conservative treatments such as physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and activity modification. However, extensive tears, full-thickness ruptures, or those causing significant weakness often necessitate surgical repair. An orthopedic specialist assesses tear size, tendon quality, patient age, and activity level to recommend the most appropriate approach.
What are the latest surgical innovations for massive or irreparable rotator cuff tears?
Recent advances include superior capsular reconstruction (SCR), tendon transfers (e.g., latissimus dorsi or pectoralis major), and biologic augmentations using platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or stem cells. SCR restores shoulder stability by reconstructing the superior capsule, while tendon transfers compensate for lost rotator cuff function. Biologic therapies aim to enhance tendon healing but are adjuncts rather than standalone treatments. These options require specialized surgical expertise and patient-specific planning.
How important is postoperative rehabilitation after rotator cuff surgery?
Rehabilitation is critical for successful recovery. Tailored protocols that consider individual factors such as tear chronicity and patient health guide the timing and intensity of passive and active exercises. Neuromuscular re-education helps restore proprioception and dynamic stability, reducing re-injury risk. Emerging modalities like biofeedback and virtual reality-assisted therapy can further enhance engagement and functional outcomes.
Can early orthopedic care reduce the need for surgery?
Yes, early diagnosis and conservative management can often halt tear progression and improve healing potential, potentially avoiding surgery. Prompt consultation allows for targeted physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments that reduce strain on the rotator cuff. However, some tears inevitably require surgical intervention despite early care, underscoring the importance of individualized treatment plans.
What factors influence healing outcomes after rotator cuff repair?
Several factors impact recovery including patient age, tear size and chronicity, comorbidities like diabetes or smoking, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration of the rotator cuff muscles can negatively affect tendon healing. Orthopedic specialists evaluate these variables to provide realistic prognosis and customize care plans.
How do orthopedic doctors differentiate between simple and complex rotator cuff tears?
Complex tears often involve multiple tendons, tendon retraction, muscle atrophy, or fatty degeneration, which require advanced imaging such as 3D MRI reconstructions or dynamic ultrasound. These features affect surgical planning and prognosis. Orthopedic surgeons specializing in shoulder pathology use a comprehensive assessment to tailor treatment strategies accordingly.
What lifestyle modifications can help prevent rotator cuff injuries or aid recovery?
Ergonomic adjustments, especially for desk workers, such as proper chair height and supportive braces, reduce shoulder strain. Avoiding repetitive overhead activities, maintaining good posture, and engaging in shoulder-strengthening exercises promote rotator cuff health. Post-injury, gradual return to activity under professional guidance minimizes re-injury risk.
What risks and complications should patients be aware of when considering rotator cuff surgery?
Potential risks include postoperative stiffness, infection, retear or failure of repair, and persistent pain. Smoking, diabetes, and poor tissue quality increase these risks. Open communication with the orthopedic team about expectations, risks, and rehabilitation commitment is essential for informed decision-making and optimal outcomes.
How does shared decision-making benefit patients with rotator cuff tears?
Shared decision-making involves collaboration between patient and orthopedic specialist to weigh treatment options, risks, and personal goals. This approach leads to personalized care plans that align with patient values and lifestyle, improving satisfaction and adherence to treatment, ultimately enhancing recovery success.
Trusted External Sources
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) – Provides comprehensive, evidence-based information on rotator cuff pathology, treatment guidelines, and patient education resources essential for understanding standard of care and outcomes (AAOS Rotator Cuff Tear Info).
- Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery (JSES) – Publishes peer-reviewed research on advanced surgical techniques, biologic augmentation, and rehabilitation protocols, offering cutting-edge clinical evidence for complex rotator cuff management (Biologic Augmentation in Rotator Cuff Repair).
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) – Offers authoritative insights into musculoskeletal conditions, patient-friendly explanations, and updates on ongoing research relevant to rotator cuff injuries and therapies.
- Orthopaedic Research Society (ORS) – A hub for emerging scientific advances in tendon biology, biomechanics, and regenerative medicine that inform future treatment approaches for rotator cuff tears.
- American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) – Provides best practice guidelines for postoperative rehabilitation and conservative management strategies, emphasizing patient-centered care and functional recovery.
Conclusion
Rotator cuff tears represent a spectrum of shoulder injuries with varying complexity that demand timely diagnosis and individualized treatment strategies. Early orthopedic consultation is paramount to identify subtle symptoms, initiate appropriate conservative care, and prevent progression to debilitating tears. Advances in surgical techniques and biologic augmentations offer promising solutions for complex and massive tears, while tailored rehabilitation protocols maximize functional recovery. Patient-centered decision-making that balances risks, benefits, and personal goals underpins successful outcomes. By integrating expert orthopedic care with lifestyle modifications and informed patient engagement, individuals can effectively navigate rotator cuff injuries toward restored shoulder function and improved quality of life. Share your experiences or questions below to foster community learning, and explore our related expert content to deepen your understanding and empower your recovery journey.

Reading this post really highlighted how crucial it is not to underplay those nagging shoulder aches or subtle weakness. I remember a time when I had persistent discomfort in my shoulder for a couple of months but brushed it off thinking it was just overuse from my gym workouts. Eventually, when the pain worsened and I struggled with simple tasks like reaching for a shelf, I consulted an orthopedic specialist. Early imaging revealed a partial rotator cuff tear, and thanks to timely physical therapy guided by the doctor, I avoided surgery altogether. This experience taught me that delaying professional evaluation can sometimes lead to more complicated injuries and longer recovery times.
The point about ergonomic adjustments for desk workers also resonates with me since I spend long hours at the computer. Small changes, like raising my monitor and taking short stretch breaks, have made a noticeable difference in easing shoulder tension.
I’m curious how others have managed the decision between continuing conservative care and moving towards surgery, especially if pain and weakness linger but aren’t severely debilitating. How do you personally balance patience with seeking more invasive treatment?
Laura, your reflection on balancing conservative care and surgery really hits home for many dealing with rotator cuff issues. From my experience, especially after witnessing a family member navigate this exact dilemma, patience with conservative treatment is essential but needs clear timelines and goals. If pain or functional limitations plateau or worsen after a few months of targeted physical therapy, it’s often a sign to consider surgical evaluation. I think what’s crucial is ongoing communication with the orthopedic specialist to monitor changes and tailor interventions accordingly. Also, I found that lifestyle adjustments—like ergonomic improvements and gradual activity modifications—play a pivotal role alongside therapy to reduce strain and support healing.
This post’s emphasis on early orthopedic consultation resonated deeply with me. Many tend to dismiss those subtle symptoms, not realizing that early evaluative imaging can distinguish between minor inflammation and partial tendon damage, which, if caught early, often means avoiding surgery altogether.
I’m curious whether others have found integrating technology, such as wearable devices or guided physical therapy apps, helpful in tracking progress and deciding when to escalate care? The decision matrix between conservative and surgical options can be daunting, and tools that provide objective feedback might empower patients to make more informed choices.